
- #POSTGRESQL YUM REPO HOW TO#
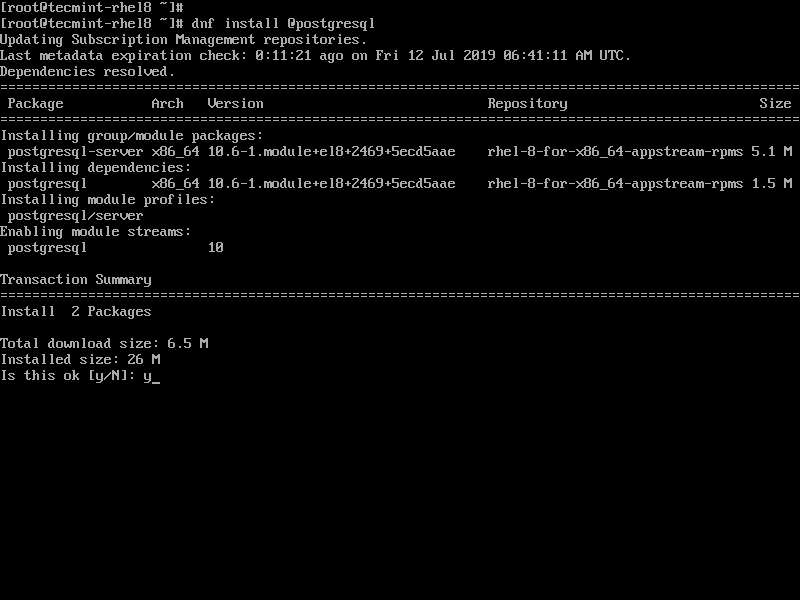
- #POSTGRESQL YUM REPO INSTALL#
- #POSTGRESQL YUM REPO UPDATE#
- #POSTGRESQL YUM REPO MANUAL#
The open-source nature of this relational database management system has kept it under an active development status for over 30 years.
#POSTGRESQL YUM REPO MANUAL#
Method supports only manual verification of packages.PostgreSQL is a well-known object-relational database system. The GitLab Runner project uses dpkg-sig tool for signing and verifying signatures on packages. The DEB format does not officially contain a default and included method for signing packages. The package signing public key can be imported from (for the stable release) or /etc//runner_unstable.repo (for the unstable releases). The repository file for RPM based distributions will be named /etc//runner_gitlab-runner.repo The public key package that should be installed is named gpg-pubkey-35dfa027-60ba0235. Verification for RPM-based distributions in the Omnibus GitLab documentation.
#POSTGRESQL YUM REPO HOW TO#
You can find the technical description of how to configure package signature Integrated with the package management systems based upon that format.
The RPM format contains a full implementation of GPG signing functionality, and thus is fully The GitLab Runner project uses its own key pair for this GPG keys used for packages signature verification can be different for each of the repositories So users wanting to have this kind of verification may need to adjust the configuration. Packages signing verification is enabled by default only in some of the DEB/RPM based distributions, Will prove that its origin is authenticated and its integrity was not violated. The build environment and the secrecy of the used GPG key, the valid signature on the package With package signing, each package is signed when it’s built. Verified until the metadata transfer from repository to the user was not affected. Whatever was uploaded to - authorized or not - will be properly It does not prove the integrity of the packages themselves. Repository metadata signing proves that the downloaded version information originatesĪt.
#POSTGRESQL YUM REPO UPDATE#
The details about the currently used key and technical description of how to update the key whenĪll keys used in the past. We use one key for all our projects hosted under.
#POSTGRESQL YUM REPO INSTALL#
For key updates in the future,Įxisting users need to manually download and install the new keys. On first installation done with the instructions above. GPG public keys used for package metadata signature verification are installed automatically Until the problem that caused the signature mismatch is found and resolved. This means that you cannot download and install any package from the repository
Verification failure should also cause the package manager to reject the Information about available packages is updated before any package is downloaded and The signature is verified when you use a command like apt-get update, so the The package manager uses repository metadata signing. To verify that the package information downloaded from the remote repository can be trusted, Two types of GPG signatures for the package installation method: repository metadata To increase user’s confidence about installed software, the GitLab Runner project provides Distribution Support Information Debian Ubuntu LinuxMint Raspbian RHEL Oracle Linux Fedora Amazon Linux You may also be able to install GitLab Runner as a binary. For example, Deepin is a Debian derivative, so the runner Debian package should install and run on Deepin. This refers to distributions that are derivative of a supported GitLab Runner distribution and that have compatible package repositories. New runner deb or rpm packages for new OS distribution releases are added automatically when supported by packagecloud.ĭepending on your setup, other deb or rpm based distributions may also be supported. We provide packages for the following supported versions of Linux distributions with packagecloud.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
